

The electron transport protein, plastocyanin helps to transport the electrons to PSI. The hydrogen ions are pumped into the inner thylakoid lumen in the chloroplast by increasing its concentration in the thylakoid lumen that can be used to make ATP. In the chloroplasts, ATP synthase is embedded into the thylakoid membrane. As the molecules pass the electrons in the electron transport chain, they pump hydrogen ions from the stroma to the thylakoid lumen. The thylakoid lumen has proteins involves in the processing of proteins, defense, redox reactions, and photosynthesis. The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase is used to generate ATP. This process generates electrons which are required for the electron transport chains. From the sunlight, the energy is utilized for splitting the water. In photolysis of water, the first step takes place in the site of the lumen of the membrane thylakoid.

This is highly reached through the generation of the carotenoid zeaxanthin and reorganization of light-harvesting complex II, both mechanisms that are stimulated by thylakoid lumen acidification.ĭuring the photosynthesis process, the lumen of thylakoid plays a major role in photophosphorylation. The non-protein quenching process is reversible and spontaneous, and it processes the dissipation of light energy absorbed as heat.

A lack of cysteine synthase 26 results in the strong photo-inhibition and systemic reactive oxygen species responses that were accompanied by decreased levels of oxygen-evolving complex proteins and assembly factors of photosystem II. In response to the oxidative stress, the cysteine synthase 26 present in a decreased amount in the lumen of thylakoid, but it has a major role in the deletion mutation of luminal redox conditions, specifically in long photoperiods. For protecting the machinery of photosynthesis amidst light conditions, plants utilize the energy dissipation processes that are partially present in the thylakoid lumen. The energy harvested by light-harvesting complex II in naturally fluctuating light conditions can be unbalanced in accordance to the stromal acceptor capacity, so the electron transport chain saturating and producing reactive oxygen species can produce photo-damage of proteins in the membrane. There is a total of three layers that are needed to be crossed while traveling from the cytoplasm to the thylakoid lumen. When the molecule is moving from cytosol to the thylakoid lumen, then it must cross the two membranes of the chloroplast and thylakoid membrane. The thylakoid lumen contains the oxygen-evolving complex and plastocyanin. The chlorophyll captures energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy which is stored in adenosine triphosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate molecules. The thylakoid membrane surrounds the thylakoid lumen. Thylakoids are the site of light reactions. Each granum is composed of a stack of 10-20 thylakoids. About 10-100 grana are suspended in the stroma. Stroma is the fluid region of the chloroplast that is enclosed by two membranes.
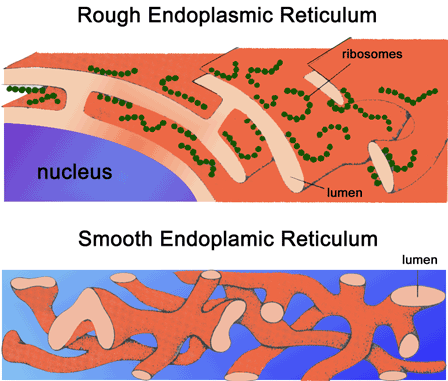
The two membranes of the chloroplast are named as outer membrane and inner membrane. The chloroplast is the organelle that is present exclusively in plant cells and functions as the site for photosynthesis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
